By the bioMérieux Connection Editors
As the COVID-19 pandemic has proven, diagnostics play an extremely important and sometimes overlooked role in providing healthcare worldwide. Bringing diagnostic solutions to market that are safe and effective is a time- and labor-intensive process that is nevertheless critical for public health, whether the solutions help address new infectious diseases or ongoing issues like antimicrobial resistance. Companies and organizations that provide diagnostics serve an important role and must overcome many challenges inherent to developing diagnostic solutions. These areas include research and development, the regulatory environment, production and manufacturing, commercialization, and insurance and reimbursement.
Research and Development
The research and development (R&D) process is critical for bringing all kinds of medical advancements, including diagnostics, to patients, where they will ultimately make an impact on healthcare. The process is complex, and researchers must experiment, iterate, and build on existing knowledge and technologies. As in all research and science, many proposed solutions do not work out, either because they are ineffective, unsafe, or both. The R&D process is specifically designed to test both the efficacy and safety of diagnostic solutions so that only the tests that meet those requirements make it into the hands of healthcare professionals.
Regulatory Environment

The purpose of regulations is to protect patients and consumers by providing a framework that all companies in a country or group of countries must use to ensure their products are safe and effective. While the goals of regulations are the same, the ways they are implemented and the processes involved differ between countries, so companies that sell their products internationally must contend with multiple sets of regulations to ensure they meet each country’s requirements. This is true for normal regulations and for those that pertain to emergency situations, such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets regulatory standards for medical products, including diagnostics. Other government organizations, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also play a role in regulation in areas such as factory design. Regulations apply not only to companies, but also to healthcare providers, and these requirements can have a cascading effect on companies that provide diagnostic and other medical solutions. The reason for this range in regulations is to cover points where a patient’s health has the potential to be adversely impacted, and to keep everyone as safe as possible.
Production and Manufacturing
In addition to meeting regulatory requirements for production and manufacturing, diagnostic companies implement their own quality assurance and safety protocols. Designing the manufacturing process for diagnostic tests requires combining those regulations and protocols with knowledge of logistics, supply chains, chemistry, and engineering. Done successfully, this process allows diagnostic companies to efficiently produce high-quality products at large volumes and meet public health demands.
Periodically, companies need to expand their production capacity. Achieving incremental increases can be accomplished in different ways, such as increasing operating hours or analyzing existing manufacturing systems and adjusting to improve efficiency. However, those are not always sufficient. If a company needs to significantly expand production or plans to make a completely new product, then manufacturing equipment and personnel must be added, or in some cases, new facilities must be built. Both can take a significant amount of time—a new factory or facility can take two or more years to be completed, because quality standards must be maintained every step of the way.
Commercialization

Countries have different environments, resources, levels of market maturity, and access when it comes to delivering healthcare to patients. Additionally, individual healthcare providers and labs differ in their capacities and capabilities. Although no company can be everything to everyone, companies that produce diagnostic tests must still be prepared to meet a wide range of needs to support public health worldwide. These considerations can affect research and development, production and manufacturing, and distribution.
Insurance and Reimbursement
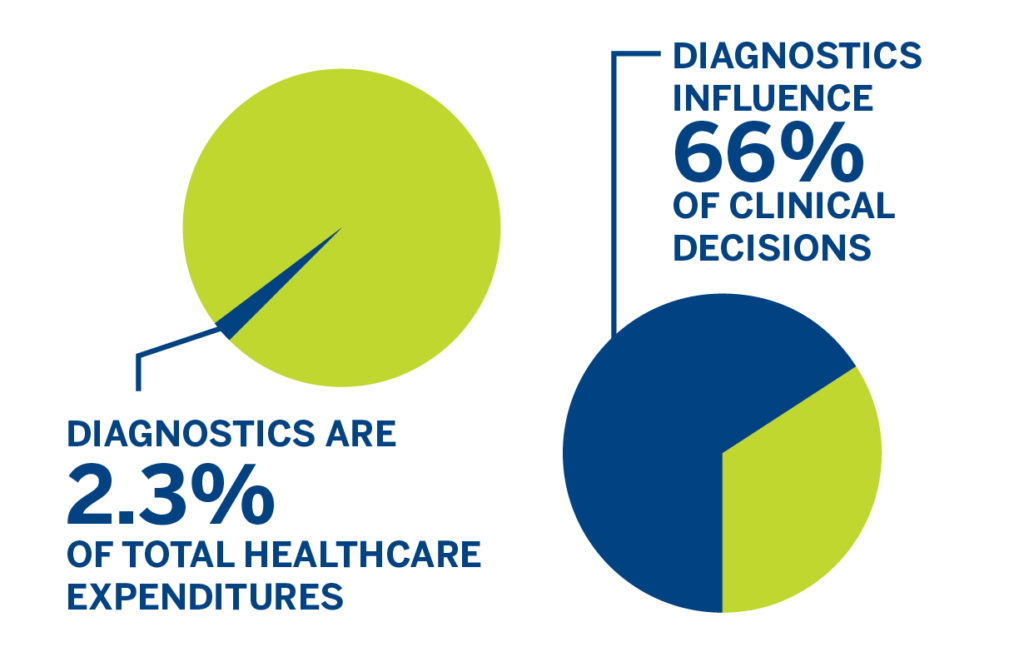
A 2016 paper reported that in vitro diagnostics represent only 2.3% of healthcare expenditures in the United States but influence 66% of clinical decisions. Additionally, the paper found indications that in vitro diagnostic tools are more often under-utilized than over-utilized. Reasons for under-utilization vary and are multifactorial, but the paper lists incentives from health insurers and reimbursement restrictions as among the causes.
Health insurance and reimbursement are highly variable, not only between countries, but all the way down to the local level. Reimbursement structures can incentivize or disincentivize the use and implementation of medical products of all kinds, including diagnostics. Furthermore, those incentives may or may not align with public health goals. For example, it has been shown that reimbursement structures for antibiotics have contributed to a substantial decrease in the number of new antibiotics in the development pipeline, which is a major concern in the face of rising antimicrobial resistance. This example demonstrates why it’s important to make sure that reimbursement structures, whether they address antibiotics, medical devices, diagnostics, or other healthcare products and services, align with public health goals across the board.
The Future of Diagnostics and Public Health
To meet the public health challenges of today and tomorrow, diagnostics companies will need to continue to innovate and work through the appropriate processes and channels to ensure that products meet the needs of patients and healthcare providers. Diagnostic tests are necessary to help understand diseases and guide medical decision-making, which ultimately saves lives. While COVID-19 has been occupying much of our conversation, it is imperative to consider the threats of antimicrobial resistance and of future pandemics. Addressing both will require collaboration across governments and the healthcare industry, including leadership and expertise from diagnostics companies.
Opinions in this article are not necessarily those of bioMérieux, Inc.



